
We’ll talk below about why that angle is important to communicate the correct shape of methane. The second carbon-hydrogen bond in the plane of the paper is specifically drawn at ~109° from that first bond. Notice that on the structure with dash and wedge notation, one carbon-hydrogen bond points straight up from the carbon and is in the plane of the paper (indicated by the simple line). It communicates the structure of methane more clearly than a traditional Lewis structure without dash and wedge notation The correct Lewis structure with dash and wedge notation for CH 4 is depicted on the right in Figure 1. Bonds drawn with a solid triangle, or wedge, represent bonded atoms coming out of the page/screen towards the observer bonds drawn with dashed triangle, or dash, represent bonded atoms going into the page/screen away from the observer.
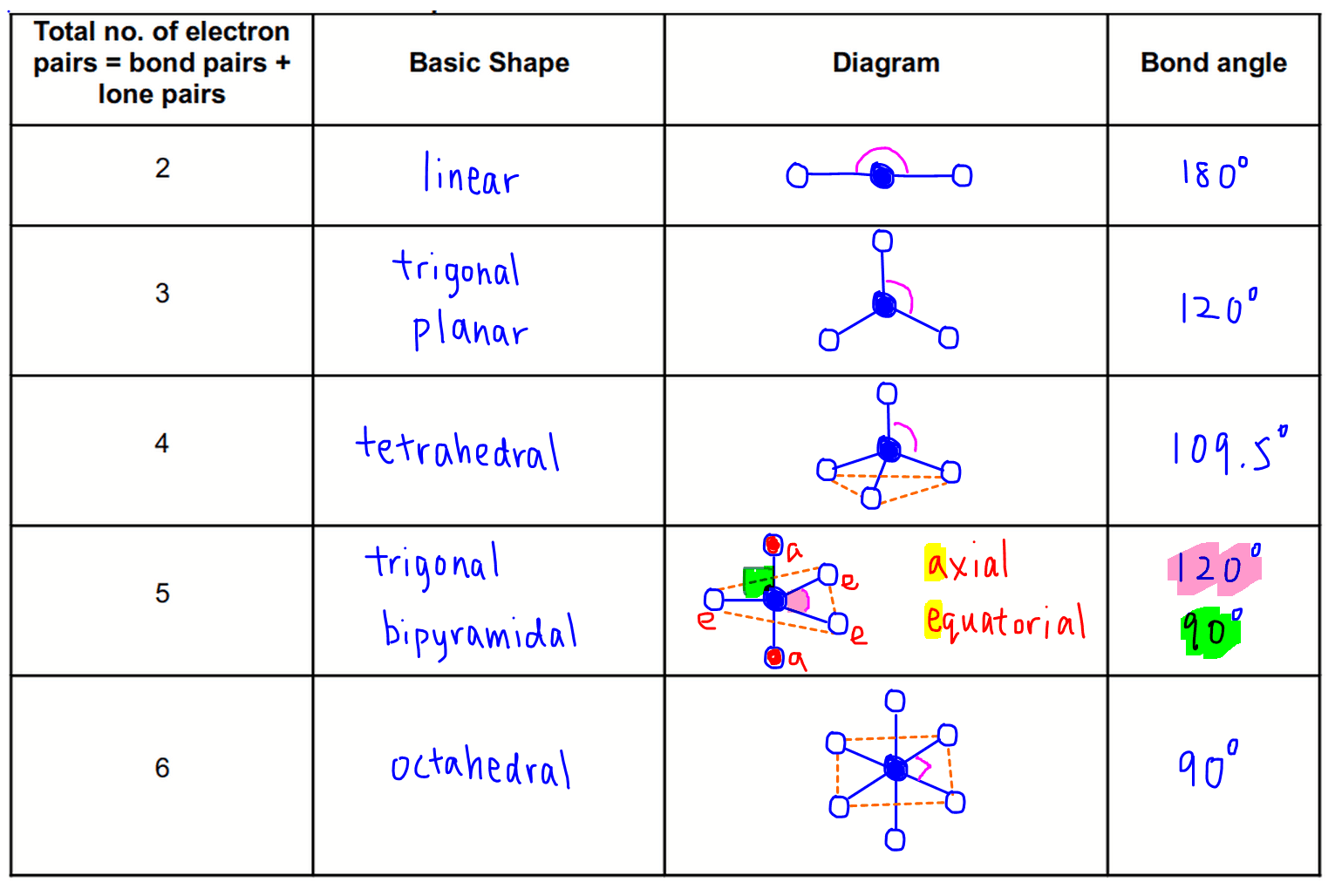
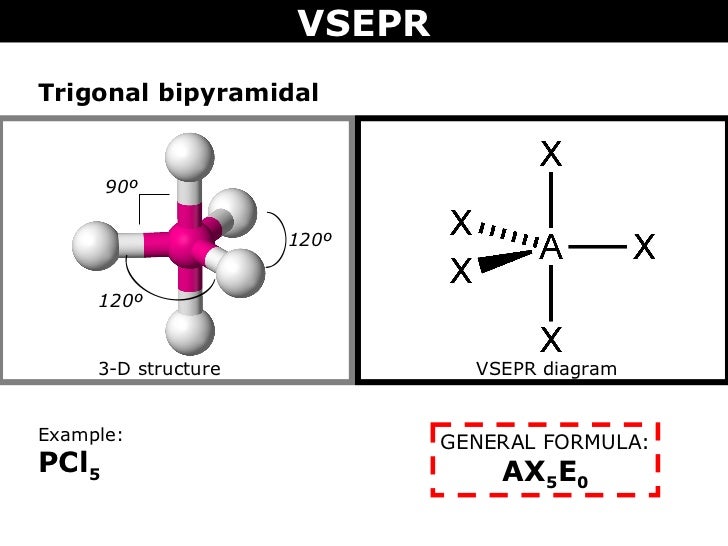
Bonds drawn as simple lines are located in the plane of the page or screen. Chemists use dash and wedge notation to draw 3D molecules. Representing three dimensions on 2D paper (or computer screen) is challenging. The Lewis structure is misleading because it depicts methane as a planar ‘plus-shaped’ molecule, yet we know that methane is a non-planar, tetrahedral molecule. Methane (CH 4) depicted by a Lewis structure (left) and dash and wedge notation (right). Depicted on the left in Figure 1 is the Lewis structure for methane (CH 4) showing the central carbon atom singly bonded to four hydrogen atoms: Figure 1. The Lewis structure gives us meaningful information about the bonds between atoms, but Lewis structures do not depict how the molecule exists in three-dimensions. | Key Concepts and Summary | Glossary | End of Section Exercises | Lewis Structures with Wedge-Dash Notation | Lewis Structures with Wedge-Dash Notations | Draw and interpret 3-dimensional representations of molecules using “dashed” and “wedge” bonds and estimate bond angles.Molecular Geometry | Predicting Electron-pair Geometry and Molecular Geometry | VSEPR Review Chart | | VSEPR Theory | Electron-pair Geometry vs. Predict molecular shape as determined by Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR).All positions are chemically equivalent, so all electronic interactions are equivalent. (This rule is more important than rule 1, so it overrules it because it has lone pairs. From Figure \(\PageIndex\) can result from differences in repulsion between various regions of electron density. Other interactions, such as nuclear-nuclear repulsions and nuclear-electron attractions, are also involved in the final arrangement that atoms adopt in a particular molecular structure. The model states that electron pairs will repel each other such that the shape of the molecule will adjust so that the valence electron-pairs stay as far apart from each other as possible. The central atom, sulfur, has 6 valence electrons, as does each oxygen atom.
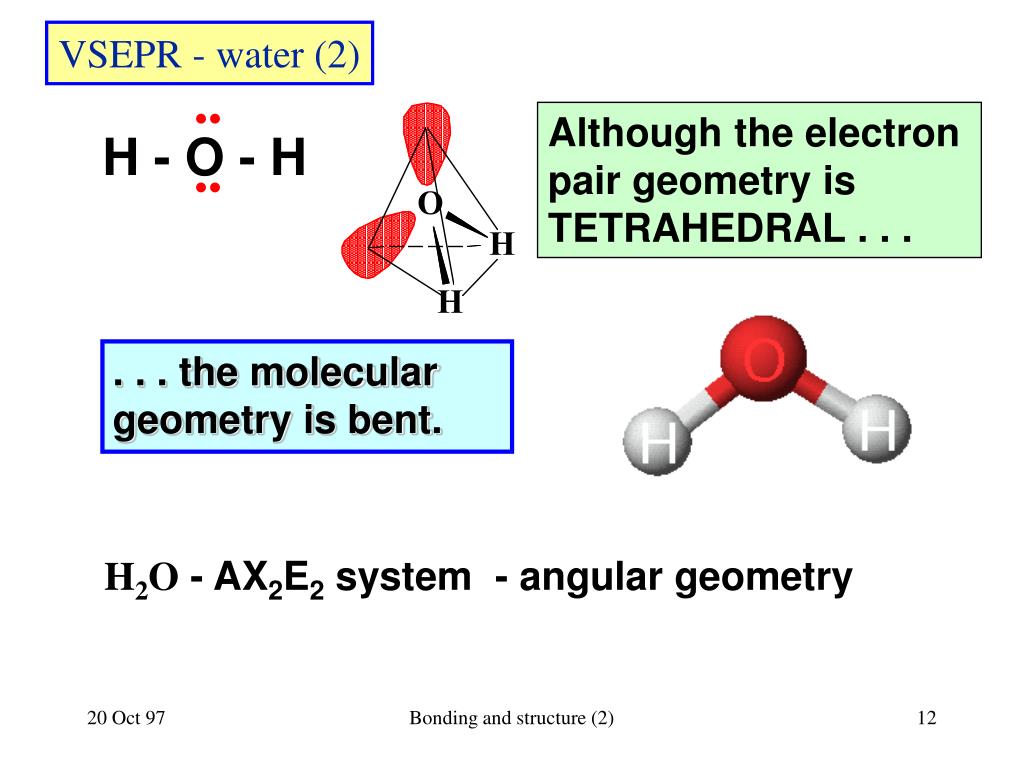
What are the electron-pair geometry and molecular structure of this polyatomic ion? Answers will vary. In an octahedral arrangement with two lone pairs, repulsion is minimized when the lone pairs are on opposite sides of the central atom. Click the card to flip Flashcards Learn Test Match Created by Andrea636 Terms in this set (27) Valence In addition, there was significant damage to livestock and crops. Therefore, we can draw a cross bow arrow towards Oxygen. The cross base arrow demonstrates the net dipole. VSEPR focuses not only on electron pairs, but it also focus on electron groups as a whole. The basic geometry is trigonal planar with 120 bond angles, but we see that the double bond causes slightly larger angles (121), and the angle between the single bonds is slightly smaller (118). Generally, a negative person is seen as bad or mean and you don't want to talk to a negative person. It is useful for nearly all compounds that have a central atom that is not a metal. Which molecule(s) has a net dipole moment? We need to comprehend electronegativity which is abbreviated EN. When drawing covalent molecules, remember that the electrons are shared between two atoms, forming a covalent bond. What is the VSEPR Theory? O lone pairs only. In the VSEPR model, the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AXmEn designation, where A is the central atom, X is a bonded atom, E is a nonbonding valence electron group (usually a lone pair of electrons), and m and n are integers. On the cross-base arrow, the cross represents the positive charge and the arrow represents the negative charge. Then, with the Lewis structure, we apply the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSPER) theory to determine the molecular geometry and the electron-group geometry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
